FDA Greenlights PTC Therapeutics’ Kebilidi for AADC Deficiency
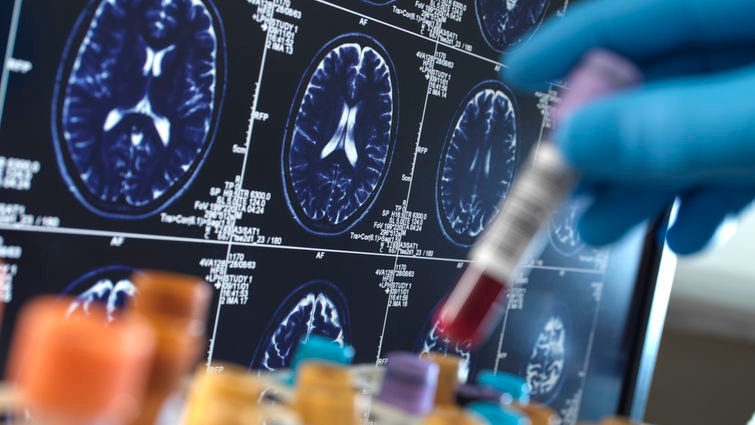
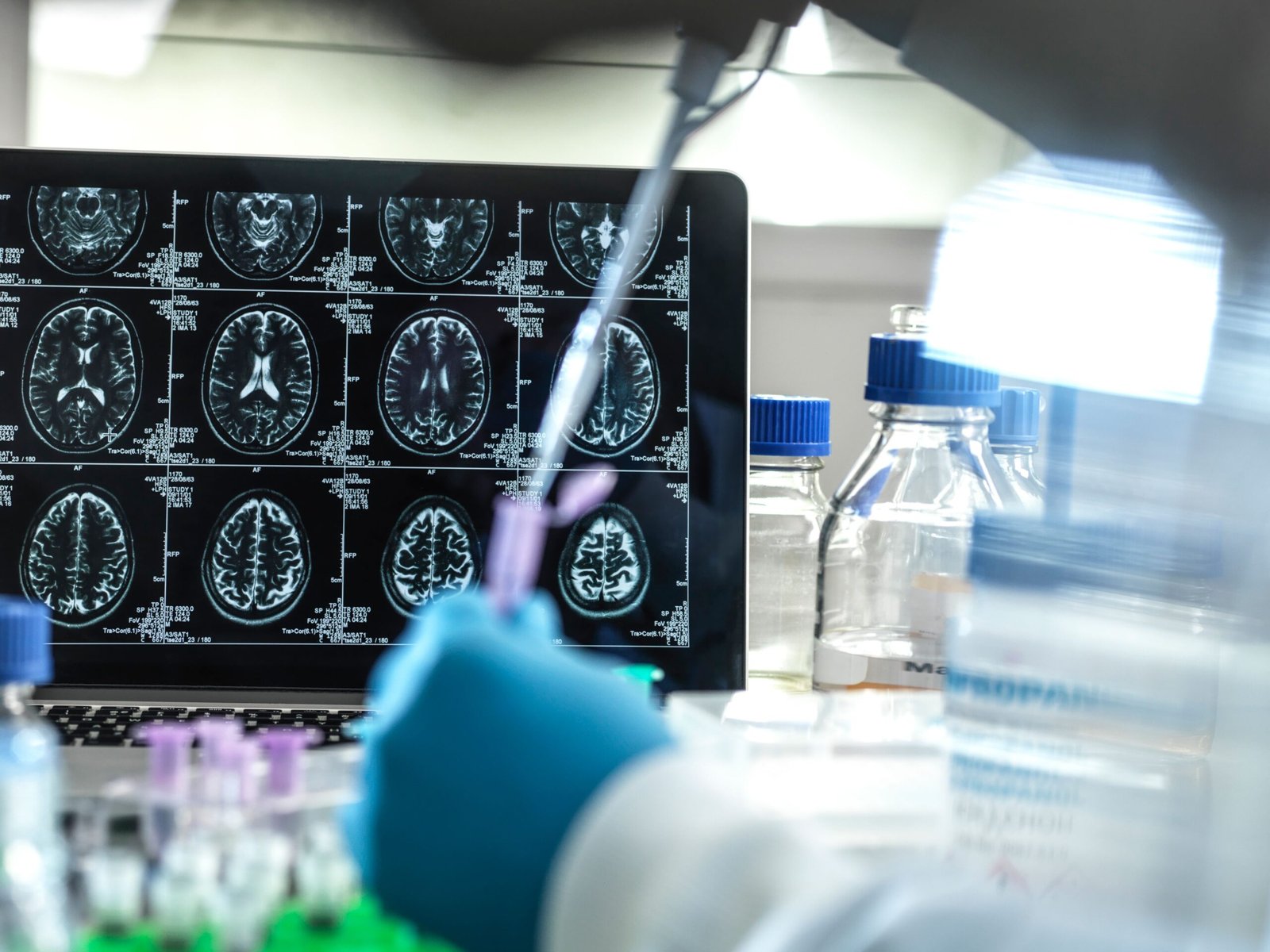
In a landmark regulatory decision, the FDA approved Kebilidi (eladocagene exuparvovec), the first gene therapy treatment for aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase (AADC) deficiency, a rare and debilitating pediatric neurological disorder. This approval on November 13, 2024, marks a critical advancement in genetic medicine, aiming to correct the underlying enzyme deficiency responsible for severe motor and developmental impairments.
Kebilidi uses AAV vector technology to deliver a functional copy of the DDC gene to patients’ brain cells, potentially restoring dopamine production and improving motor function. Clinical trials demonstrated substantial improvements in motor milestones and quality of life for treated children, representing hope for families facing this life-altering condition. The therapy’s prioritization by the FDA underscores its potential to transform treatment paradigms for rare genetic diseases.
Emerging Progress in Immune-Oncology Therapeutics
Concurrent with the FDA approval news, significant progress was reported in immune-oncology. Researchers and biotech companies continue to develop and refine immunotherapy candidates that harness the body’s immune system against cancer with enhanced specificity and efficacy.
Novel therapeutic strategies combining immune checkpoint inhibitors with vaccines or other biologics are showing promise in cancers notoriously resistant to conventional treatments. These advances reflect growing sophistication in the design of combination therapies aimed at durable tumor control while reducing adverse effects. The integration of biomarker-driven patient selection is further personalizing treatment approaches, accelerating clinical success.
NIH Hosts Workshops to Shape Future Pain Therapeutics Development
On November 13, 2024, the National Institutes of Health (NIH) hosted a series of workshops focused on informing the strategic priorities of the NIH HEAL Initiative, a bold effort to combat opioid addiction and chronic pain.
These workshops gathered stakeholders from academia, industry, and government to discuss innovative approaches for non-addictive pain therapeutics development. Key themes included identifying novel drug targets, leveraging precision medicine, and enhancing clinical trial design to accelerate safe therapies to patients. The NIH’s commitment to fostering collaboration and innovation is expected to catalyze new treatments that could revolutionize pain management and reduce reliance on opioids.
This comprehensive news article highlights pivotal FDA regulatory progress, promising immunotherapy advancements, and strategic federal initiatives shaping the clinical research landscape as of November 13, 2024. It offers your readers insightful, relevant content reflecting key biopharmaceutical and clinical trial developments.